epoll
Explains Kernel epoll interface
Jul 13, 2025
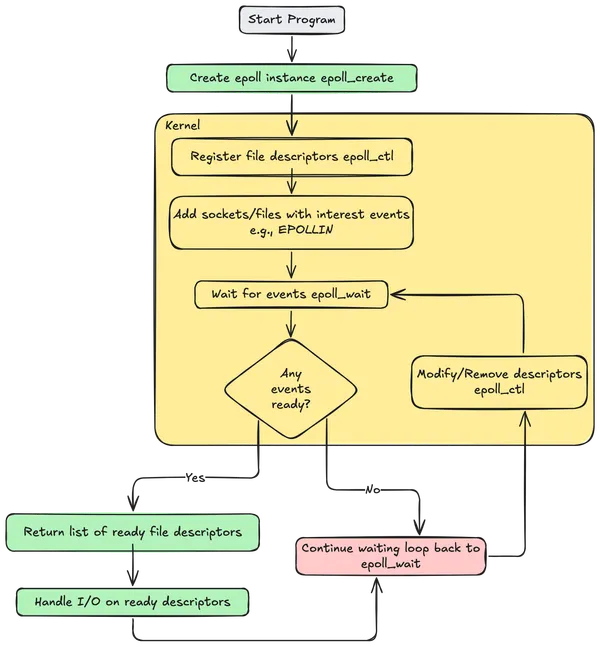
epoll allows a single thread or process to register interest in a long list of file descriptors. A call to epoll_wait will then block until one of those descriptors is ready for reading or writing. A single thread using epoll can handle tens of thousands of concurrent (and mostly idle) requests.
Original proposal: http://www.xmailserver.org/linux-patches/nio-improve.html
The central concept of the epoll API is the epoll instance, an in-kernel data structure which, from a user-space perspective, can be considered a container for two lists:
-
The interest list (sometimes also called the epoll set): the set of file descriptors that the process has registered an interest in monitoring.
-
The ready list: the set of file descriptors that are “ready” for I/O. The ready list is a subset of (or, more precisely, a set of references to) the file descriptors in the interest list. It is dynamically populated by the kernel as a result of I/O activity on those descriptors.
API
epoll_create and epoll_create1
These functions are used to create a new epoll instance or, as the manual says, to “open an epoll file descriptor.” When epoll_create or epoll_create1 is called, the kernel creates a new epoll instance, a special data structure inside the kernel.
The file descriptor returned for the epoll instance can be used to add, remove, or modify the file descriptors that should be monitored for I/O.
epoll_ctl
Used to add, modify, or remove entries in the interest list of the epoll instance referred to by the file descriptor epfd. It requests that the operation op be performed on the target file descriptor fd.
epoll_wait
Waits for events on the epoll instance referred to by the file descriptor epfd.
The buffer pointed to by events is used to return information from the ready list about file descriptors in the interest list that have events available. Up to maxevents entries are returned by epoll_wait(). The maxevents argument must be greater than zero.
The timeout argument specifies the number of milliseconds that epoll_wait() will block. Time is measured against the CLOCK_MONOTONIC clock.
A call to epoll_wait() will block until either:
- a file descriptor delivers an event,
- the call is interrupted by a signal handler, or
- the timeout expires.