mTLS
mTLS (Mutual Transport Layer Security) is a security process that ensures traffic is secure and trusted in both directions between a client and a server.
Oct 27, 2025
mTLS (Mutual Transport Layer Security) is a process where the TLS handshake is performed only after both the client and server verify their counterpart’s certificate.
This is achieved through a two-way handshake where both parties exchange and verify digital certificates issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This ensures that both the server and the client are who they claim to be, making it more secure than traditional TLS, which only authenticates the server.
This is a bit different from the standard TLS used for websites. In that case, the browser verifies the server’s certificate, but the client (the browser) doesn’t need to present its own certificate.
How does mTLS work?
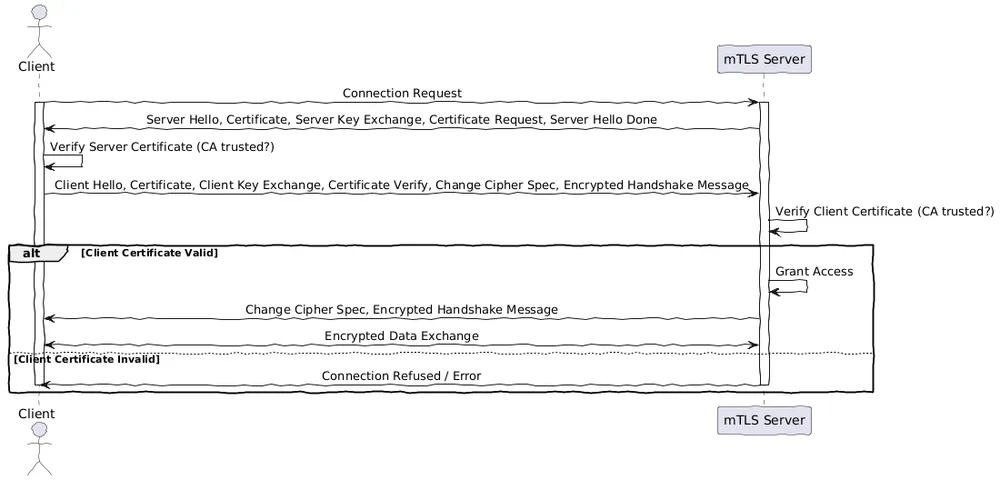
- The client connects to the server.
- The server presents its TLS certificate.
- The client verifies the server’s certificate.
- The client presents its TLS certificate.
- The server verifies the client’s certificate.
- The server grants access (if the certificate is valid).
- The client and server exchange information over an encrypted TLS connection.
mTLS helps ensure that traffic is secure and trusted in both directions between a client and a server. This helps to secure both endpoints by verifying that the intended parties are connecting between themselves and that an unauthorized party cannot pretend to be either party.
Therefore, mTLS is widely used between and within organisations to secure network perimeters, helping to create a zero-trust security model.