Consistency
A transaction must transform the database from one consistent state to another consistent state.
Nov 17, 2025
Consistency ensures that a database transaction brings the database from one valid state to another valid state, maintaining all defined rules and constraints.
- Integrity constraints must be satisfied before and after the transaction (Eg: Foreign keys constraints)
- Business rules encoded in the database are enforced
- If a transaction violates consistency rules, it’s rolled back
Example
If you transfer £200 between bank accounts, consistency ensures:
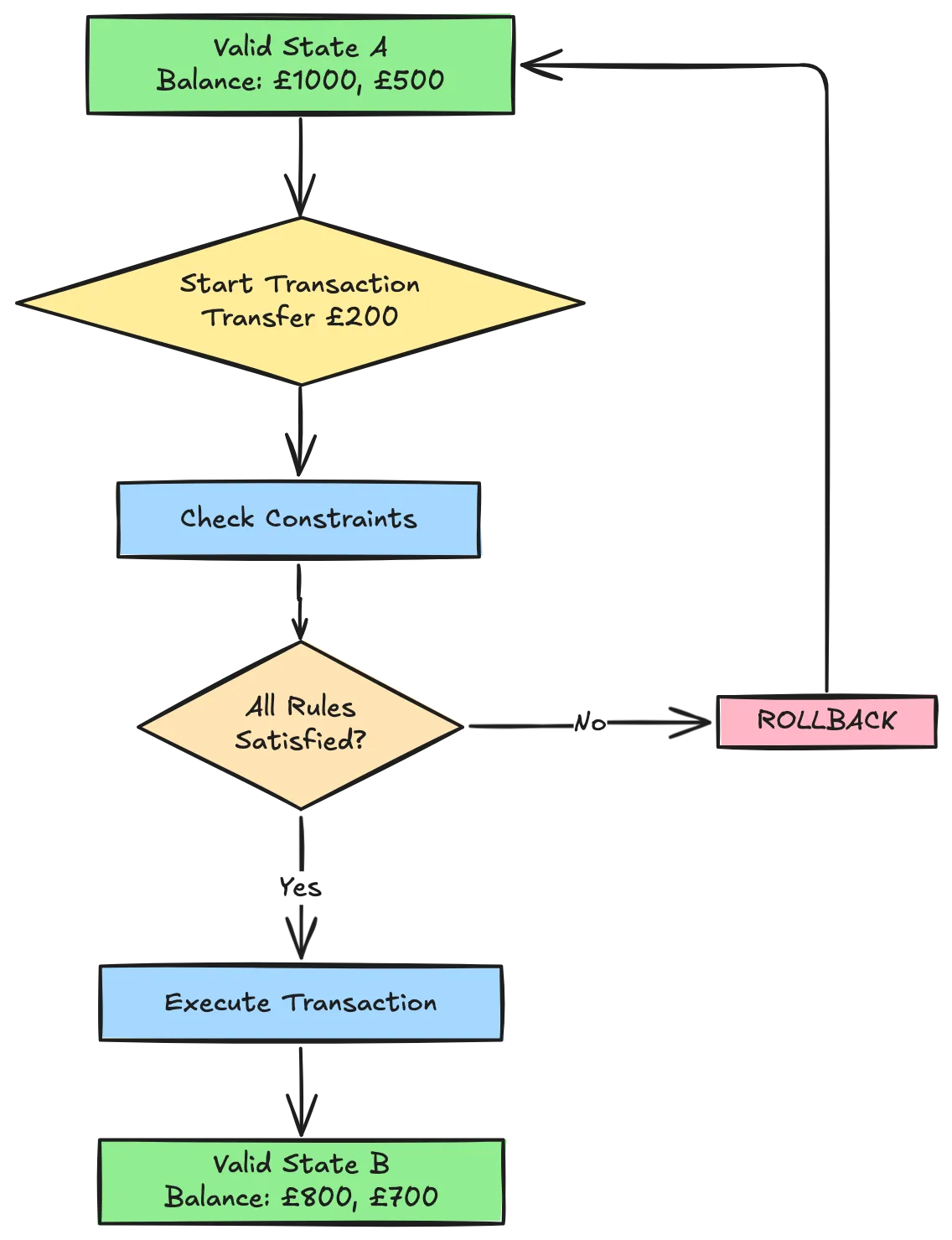
Both accounts exist
- The sender has sufficient funds
- Total money in the system remains the same
- All constraints (positive balance, valid account types) are maintained
Consistency vs Atomicity
Atomicity handles completeness of execution, Consistency handles correctness of the result.
Further Reading
Linked References
"...| | Consistency | A transaction must bring the database from one valid state to another,..."