Durability
A transaction must transform the database from one consistent state to another consistent state.
Nov 18, 2025
Durability guarantees that once a transaction is committed, it stays committed—even if the system crashes immediately after.
Committed = Permanent
Even if there’s a:
- Power outage
- System crash
- Hardware failure
- Software bug
…your data survives.
Databases use persistent storage (disks/SSDs) and techniques like:
- Write-ahead logging (WAL): Recording changes before applying them
- Transaction logs: Keeping a history for recovery
- Checkpointing: Periodically syncing memory to disk
Durability gives users confidence that their transactions won’t vanish into thin air.
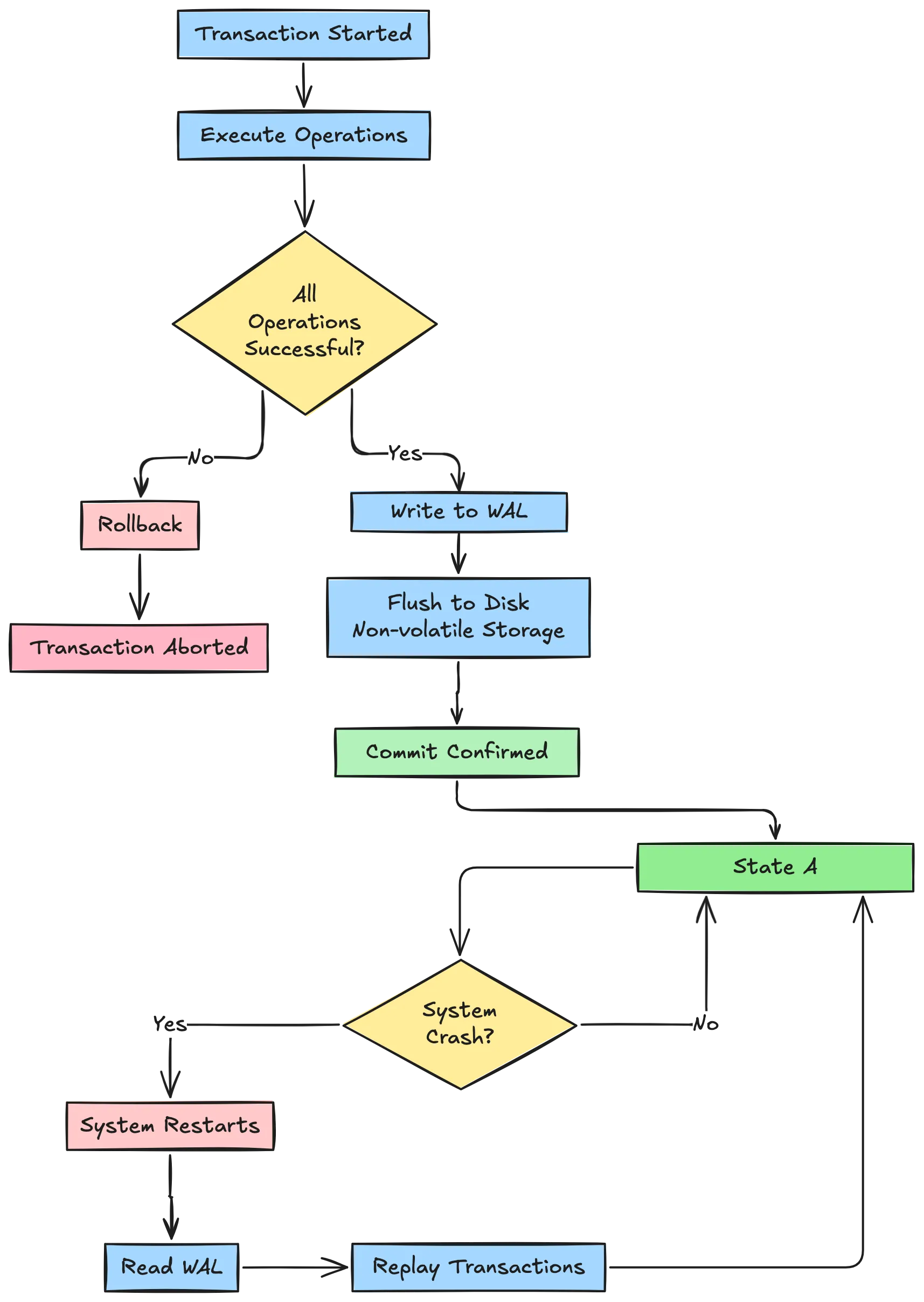
There’s a performance cost, writing to disk is slower than memory, but reliability demands it.
Consistency vs Atomicity
They’re complementary. Atomicity gives you clean transactions, durability makes them permanent.
Further Reading
Linked References
"...to 0; the other will be blocked or fail, preventing double-booking. | | Durability | Once a transaction commits, its changes must persist even in the event of..."